Horizontal analysis looks at trends over time, comparing financial data across multiple reporting periods. For example, you can use horizontal analysis to compare revenue from this year to revenue from last year. Vertical analysis shows a comparison of a line item within a statement to another line item within that same statement. This allows a business to see what percentage of cash (the comparison line item) makes up total assets (the other line item) during the period.
How Horizontal Analysis Works
Horizontal analysis, also known as trend analysis, is a financial analysis method that evaluates a company’s financial performance over multiple periods. By comparing line items in financial statements across consecutive periods, this analysis allows stakeholders to identify trends, patterns, and changes in a company’s financial position. Horizontal analysis is another financial statement analysis tool that compares distinct line items across multiple periods. This method is also known as trend analysis since it enables individuals to spot a business’s long-term financial trends.
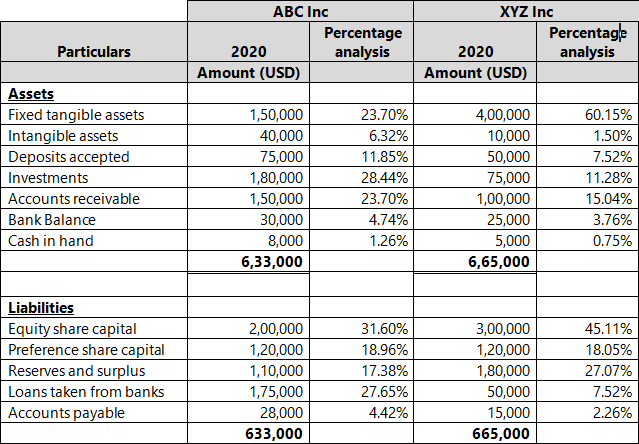
Comparison Table
- By leveraging the power of both horizontal and vertical analysis, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial health, identify areas for improvement, and drive sustainable growth.
- In this article, we will explore the attributes of horizontal analysis and vertical analysis, highlighting their key differences and benefits.
- Typically this involves stating items as a percentage of a key benchmark, allowing you to make comparisons between years.
- Placing the percentage changes on a line chart over time illustrates whether performance has increased, decreased, or remained consistent.
This allows for easy comparison across companies of different sizes or comparison of a company’s performance over multiple periods. The difference between horizontal and vertical analysis is that the former considers the total amount as a percentage in the financial statement over many consecutive years. The latter discusses each amount separately in the financial information as a percentage for another amount. Vertical and horizontal analysis are considered two distinct methods of financial analysis that serve different purposes. Besides, here are the key differences between vertical and horizontal analysis applications. While both vertical and horizontal analysis provide valuable insights into financial performance, they are also considerably different.
Advantages of Horizontal Analysis
It is used to see if any numbers are unusually high or low in comparison to the information for bracketing periods, which may then trigger a detailed investigation of the reasons for the difference. Horizontal analysis is valuable because analysts assess past performance along with the company’s current financial position or growth. Horizontal analysis can also be used to benchmark a company with competitors in the same industry.
Horizontal Analysis: What It Is vs. Vertical Analysis
Besides, finance professionals involved in financial planning, investment analysis, or corporate finance must deeply understand both analysis methods. Emeritus offers online finance courses to help finance professionals deepen their vertical and horizontal analysis knowledge and enhance their skills. Additionally, these courses cover various topics, including financial statement analysis, financial modeling, and valuation techniques. By signing up for these courses, professionals can gain skills that can be applied in their day-to-day work and advance their careers in the lucrative field of finance. Horizontal analysis can also help individuals make informed financial decisions. By comparing the same item over different periods, individuals can identify trends in a company’s financial performance and make educated judgments about allocating their resources.
Venture Capital and Private Equity: Investment Strategies
Financial Analysis is helpful in accurately ascertaining and forecasting future trends and conditions. The primary aim of horizontal analysis is to compare line items in order to ascertain the changes in trend over time. As against, the aim of vertical analysis is to ascertain the proportion of item, in relation to a common item in percentage terms. Last, a horizontal analysis can encompass calculating percentage changes from one period to the next. As a company grows, it often becomes more difficult to sustain the same rate of growth, even if the company grows in pure dollar size.
Horizontal analysis, also known as trend analysis, focuses on comparing financial data over a specific period. It involves analyzing the changes in financial statement items, such as revenues, expenses, and net income, over time. The primary objective of horizontal analysis is to identify trends, patterns, and fluctuations in financial performance.
With the help of this analysis, the percentages so computed can be directly compared with the result of the equivalent percentages of the past years or other companies operating in the same industry, irrespective of their size. So, common size financial statement not only helps in intra-firm comparison but also in inter-firm comparison. Horizontal and vertical analysis are two important methods used to analyze financial statements. This section will provide an overview of each method and highlight the key differences between them. Investors can use horizontal analysis to determine the trends in a company’s financial position and performance over time to determine whether they want to invest in that company.
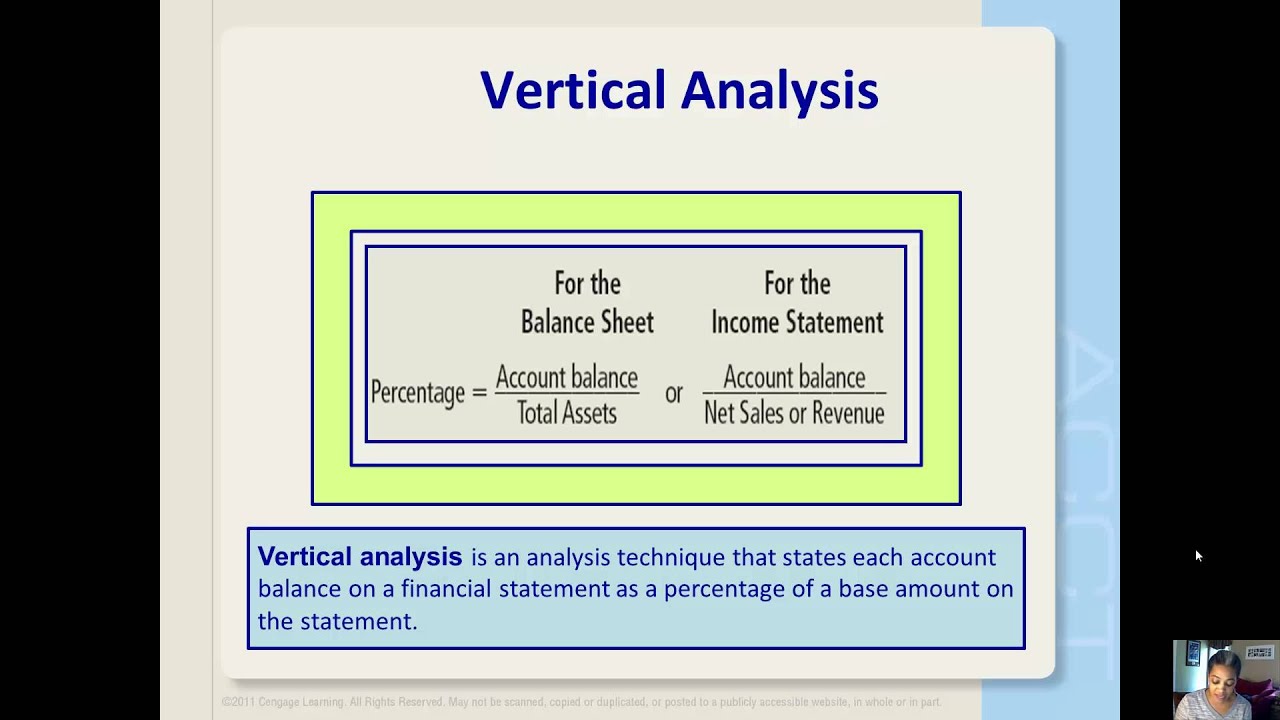
Vertical analysis looks at the contributing percentage of each line item to the total base figure. It can provide information on what metrics are improving and which are worsening. It can be used to compare different components of companies and the same company in different time periods. Also like horizontal analysis, vertical analysis can be useful in external as well as internal analysis. Two companies with vastly different financial profiles (e.g., a $10 million company and a $10 billion dollar international corporation) can still be meaningfully compared by reducing their financials to percentages. For example, horizontal analysis might show that production costs for a medical devices supplier in EMEA increased by 15% over the past 3 years.
Both, however, are important when it comes to business decisions based on the performance. Vertical analysis is a method of financial statement analysis in which each line item is listed as a percentage of a base figure within the statement. Vertical analysis is a method that examines individual line items on a financial statement as a percentage of a base figure, such as total assets or total revenue. It also allows businesses to identify trends and patterns in their financial performance over time and make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment, and strategy. For the balance sheet, total assets or total liabilities and shareholders’ equity are typically used as the base amount. Choosing an appropriate base amount allows the vertical analysis to show the composition of key financial statement items.
Learn about emerging trends and how staffing agencies can help you secure top accounting jobs of the future. We can see revenue and profits grew difference between horizontal and vertical analysis substantially while expenses grew at a lower rate. This allows us to see the relative size of each component and compare them over time.

